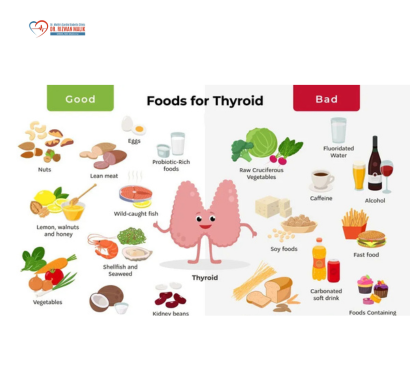
Understanding the Importance of Vaccinations Against Common Infectious Diseases
Vaccinations are one of the greatest achievements in modern medicine. They have not only reduced the spread of life-threatening diseases but also helped protect communities from deadly outbreaks. From childhood to adulthood, vaccines play a crucial role in strengthening our immune systems and preventing infections that could otherwise cause severe complications or even death. In India, where population density and diverse living conditions make the spread of infectious diseases more likely, vaccination is an essential public health tool. With increased awareness and access, vaccines continue to save millions of lives each year. In this blog, we’ll explore why vaccinations are important, how they work, the common diseases they protect us against, and how preventive measures like the HPV vaccine are shaping the future of healthcare. How Vaccines Work Vaccines prepare the immune system to recognize and fight infections. They contain weakened or inactive parts of a pathogen (virus or bacteria) that stimulate the immune system without causing illness. Once vaccinated, the body “remembers” the infection and can mount a faster, stronger response if exposed in the future. Key Functions of Vaccines: Prevention of disease – Stops infections before they occur. Reduction in complications – Lessens the risk of severe illness. Community immunity (herd immunity) – Protects those who cannot be vaccinated (such as infants or immunocompromised individuals). Disease elimination – Has led to the eradication of diseases like smallpox and near elimination of polio. Why Vaccinations Are Important Protection Against Serious Diseases Infectious diseases like measles, diphtheria, hepatitis, and influenza can be life-threatening. Vaccination reduces both the incidence and severity. Cost-Effective Healthcare Preventing disease through vaccination is far less expensive than treating severe illness and its complications. Reduced Burden on Hospitals In a country like India, where public hospitals are often overcrowded, preventing diseases through vaccination helps reduce the healthcare burden. Global Travel and Safety Vaccines protect travelers and prevent the import or export of diseases across borders. Common Infectious Diseases Prevented by Vaccines 1. Measles, Mumps, and Rubella (MMR) Highly contagious viral diseases. The MMR vaccine has drastically reduced childhood deaths worldwide. 2. Polio Once a crippling disease in India, polio has been eliminated thanks to large-scale vaccination drives. 3. Diphtheria, Tetanus, and Pertussis (DTP) Prevents throat infections, muscle stiffness, and whooping cough. 4. Hepatitis B A viral infection affecting the liver, which can cause chronic illness and liver cancer. 5. Human Papillomavirus (HPV) Linked to cervical cancer, one of the leading cancers in Indian women. The HPV vaccine is a powerful tool in reducing future cancer risks. 6. Influenza (Flu) Seasonal flu can lead to severe illness in vulnerable groups. Annual flu shots are recommended. 7. COVID-19 Recent global pandemic proved the importance of rapid vaccination in saving millions of lives. Vaccination Across Life Stages Infants & Children: Most essential stage for vaccinations like BCG, DTP, MMR, and polio. Adolescents: HPV vaccine and booster doses of earlier vaccines. Adults: Tetanus boosters, influenza, hepatitis, and COVID-19 vaccines. Elderly: Pneumococcal, influenza, and shingles vaccines for added protection. Addressing Myths and Misconceptions About Vaccines “Vaccines cause side effects.” Mild side effects like fever or swelling are temporary. Serious side effects are extremely rare. “Natural immunity is better than vaccines.” Natural infections can cause severe complications, while vaccines provide safe immunity. “Vaccines are only for children.” Adults also require vaccinations to protect against diseases like flu, shingles, and hepatitis. “If others are vaccinated, I don’t need to be.” Herd immunity only works if most people are vaccinated. Everyone plays a role in preventing outbreaks. Preventive Power of the HPV Vaccine Cervical cancer is one of the most preventable cancers, and the HPV vaccine is key to that prevention. Given to both boys and girls (preferably in adolescence), it prevents infection with HPV strains most commonly associated with cervical and other cancers. India’s increasing awareness about HPV vaccination is a huge step toward women’s health and cancer prevention. Vaccinations are not just individual protection—they are a public health responsibility. By getting vaccinated, you protect yourself, your loved ones, and the community. In India’s fight against infectious diseases, vaccines are our strongest shield. FAQs Are vaccines safe for everyone? Most vaccines are safe for all, but certain individuals with allergies, immune system issues, or specific health conditions may need to consult a doctor before vaccination. How often do adults need vaccines? Adults may require booster shots every 5–10 years for certain vaccines, and annual vaccines like flu shots. Can vaccines prevent cancer? Yes. The HPV and Hepatitis B vaccines prevent infections that can lead to cervical and liver cancers, respectively.