Diabetes
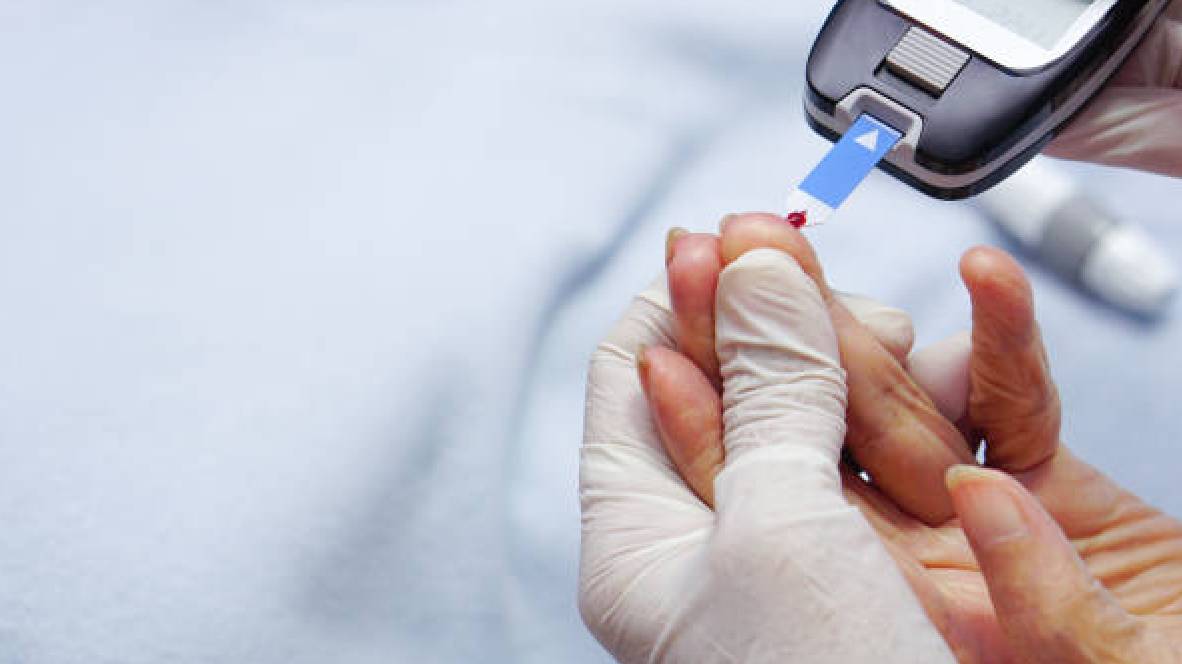
Diabetes management aims to control blood glucose levels, prevent complications, and improve quality of life for patients with diabetes. It includes medication, lifestyle changes, and regular monitoring.
Diabetes is a chronic disease that occurs either when the pancreas does not produce enough insulin or when the body cannot effectively use the insulin it produces. Insulin is a hormone that regulates blood glucose.
Typical Cases
- Type 1 Diabetes: Autoimmune destruction of insulin-producing cells in the pancreas, typically diagnosed in children and young adults.
- Type 2 Diabetes: Insulin resistance, often associated with obesity and typically diagnosed in adults.
- Gestational Diabetes: Diabetes diagnosed during pregnancy.
Symptoms and Management
- Type 1 Diabetes:
- Symptoms: Increased thirst, frequent urination, hunger, weight loss, fatigue, and blurred vision.
- Management: Insulin therapy, blood glucose monitoring, healthy eating, and physical activity.
- Type 2 Diabetes:
- Symptoms: Increased thirst, frequent urination, hunger, fatigue, blurred vision, slow-healing sores, and frequent infections.
- Management: Lifestyle changes (diet, exercise, weight loss), oral medications (metformin, sulfonylureas), and sometimes insulin.
- Gestational Diabetes:
- Symptoms: Often none; diagnosed through screening tests during pregnancy.
- Management: Blood glucose monitoring, diet changes, physical activity, and sometimes insulin or oral medications.
Monitoring
- Blood Glucose Monitoring: Regular self-monitoring of blood glucose levels using glucometers.
- HbA1c Testing: A blood test that provides an average blood glucose level over the past 2-3 months, typically done every 3-6 months.
Lifestyle Modifications
- Diet: A balanced diet with controlled carbohydrate intake, focusing on whole grains, fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats.
- Exercise: Regular physical activity to help manage blood glucose levels and improve overall health.
- Weight Management: Achieving and maintaining a healthy weight.
Medications
- Insulin: Required for Type 1 diabetes and sometimes for Type 2 diabetes, administered through injections or an insulin pump.
- Oral Hypoglycemics: Medications such as metformin, sulfonylureas, and DPP-4 inhibitors that help control blood glucose levels.
- Non-Insulin Injectables: Medications like GLP-1 receptor agonists that help lower blood glucose.
Complications Management
- Neuropathy: Managing nerve damage through medications, proper foot care, and regular check-ups.
- Retinopathy: Regular eye exams and treatment to prevent vision loss.
- Nephropathy: Monitoring kidney function and managing blood pressure to prevent kidney damage.
